In this section, we will explore the concepts of lighting. We will learn about color temperature, color reflectance percentage, luminous flux, light intensity, luminous efficacy, illuminance, reflection coefficient, and brightness.
what is color temperature
Color temperature is a numerical value that represents the brightness and color of external light, measured in Kelvin degrees. The higher this number, the closer the light’s color is to the cool and white spectrum. The lower the number, the closer the light’s color is to the warm spectrum, such as the light emitted by incandescent lamps.
Generally, a color temperature above 4000 Kelvin is considered cool light, while a color temperature below 3000 Kelvin is considered warm light.
A black body, like platinum, is an element that does not reflect any light and absorbs all the light that is incident on it.
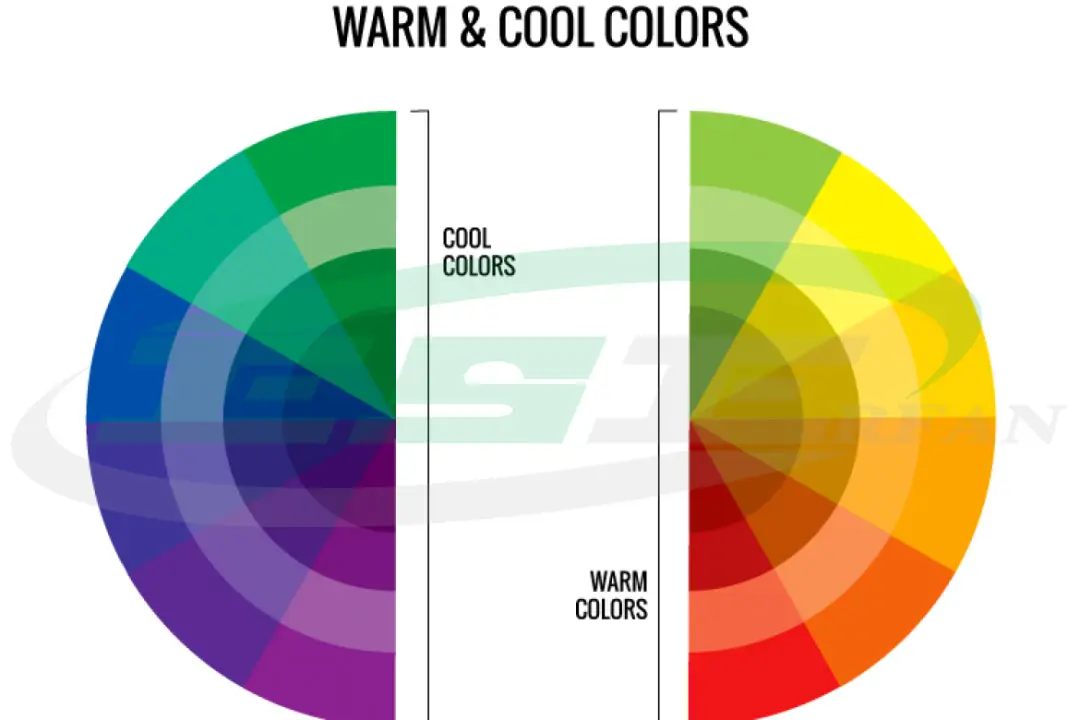
The light source is determined by comparing it to the color of an ideal black body. When a black body is heated, it initially emits light tending toward red colors. As the temperature increases, the light’s color moves toward the orange, yellow, white, and eventually blue range. The higher the temperature, the whiter the body appears.Since the concept of color temperature may be unfamiliar to many users, manufacturers have established terms to express color temperature according to standards, which are printed on the lamps. Terms such as “sunlight” or “warm white,” “neutral white” or “cool white,” and “moonlight” or “daylight” are among the commonly used terms, which are explained below.
Color Temperature Terms
Warm White (WW): The light from these lamps, with a color temperature of less than 3300 Kelvin, creates a sense of warmth and comfort in the environment. The light color of these lamps is similar to incandescent lamps. These lamps are suitable for environments such as hotels, hospitals, bedrooms, living rooms, nurseries, and conference halls, where relaxation or a sense of comfort is desired.
Neutral White (NW): The light from these lamps, with a color temperature ranging from 3300 to 5000 Kelvin, provides a color light between warm white and daylight. The light color of these lamps is similar to fluorescent lamps with neutral white light.
Daylight White (DW): These lamps produce light with a color temperature above 5000 Kelvin, making them highly suitable for places that require bright lighting. The light color of these lamps is similar to daylight fluorescent lamps.
These lamps are ideal for installation in stores, supermarkets, production industries, and factories.
Despite the variety of lamps with different color temperatures, it is often mistakenly believed that placing two lamps, one with warm white and the other with daylight white light, together will create a balanced light in an environment. However, this practice not only makes the environment unattractive but also leads to uneven light distribution, which is not ideal from a modern lighting design perspective. It is clear that using lamps with a neutral white light (such as cool white) can achieve the desired result without the need for such a combination.
Color Rendering Index (CRI):
Since the sun is considered the primary light source, the best and most natural viewing condition for humans is under sunlight. It is important to note that visually, the best light sources are those that have a light spectrum most similar to natural sunlight.
Using the reflection of objects under sunlight as a reference, the Color Rendering Index (CRI) or color reflection percentage indicates how accurately the colors of objects appear under light emitted by a lamp compared to their true colors.
CRI for lamps ranges from 20 to 100, and the higher the number, the more accurately the colors are rendered.
The main factor that determines the color rendering quality of a light source is the completeness of its light spectrum. For example, if a lamp’s emitted light spectrum lacks red color, any red objects (with red parts) will not appear in their true color.
Therefore, for places where accurate color representation is crucial, such as in textile industries, paint rooms in the automotive industry, makeup and cosmetic rooms, etc., it is recommended to use lamps with a high color rendering index.
Classification of Color Rendering Index (CRI)
According to the standard, the Color Rendering Index (CRI) is divided into six main groups:
1A: Excellent Color Rendering Index (90-100%)
1B: Very Good Color Rendering Index (80-90%)
2A: Good Color Rendering Index (70-80%)
2B: Average Color Rendering Index (60-70%)
3: Acceptable Color Rendering Index (40-60%)
4: Poor Color Rendering Index (20-40%)
The color reflection percentage in any environment is one of the factors specified by the standard.
For example, in a hospital environment, the color rendering index should fall into group 1 (i.e., 1A or 1B). Therefore, using standard fluorescent lamps, which fall into groups 2A or 2B, would not be appropriate for this purpose.
To indicate the color temperature and CRI of different lamps, in recent years, the International Association of Lighting Engineers has suggested a three-digit code (such as 827, 740, 930, etc.) for lamps. The first digit indicates the color rendering index according to the table below.
90-100% | 9
80-89% | 8
70-79% | 7
60-69% | 6
50-59% | 5
40-49% | 4
The second and third digits of this code represent the color temperature of the lamp in Kelvin units.





