Light is an electromagnetic radiation.
According to Planck’s theory, if energy is given to the electrons of an atom that are orbiting its nucleus, the electrons move out of their principal level and are transferred to a higher energy level. Given that the new level is not a stable level for these electrons, upon removal of the energy source, the electrons tend to return to their principal level. According to Planck’s theory, the energy stored during this displacement process, upon returning from a higher level to a lower level, is emitted as light in the form of energy packets called photons.
The emitted wavelength is directly proportional to the amount of energy released. This proportionality is shown with the help of a constant coefficient called Planck’s constant in the form of the following relation: E = hυ
In the above relation, h is Planck’s constant, υ is the frequency (which has an inverse relation with wavelength) of the emitted light, and E is energy.
Light Emission as Electromagnetic Waves
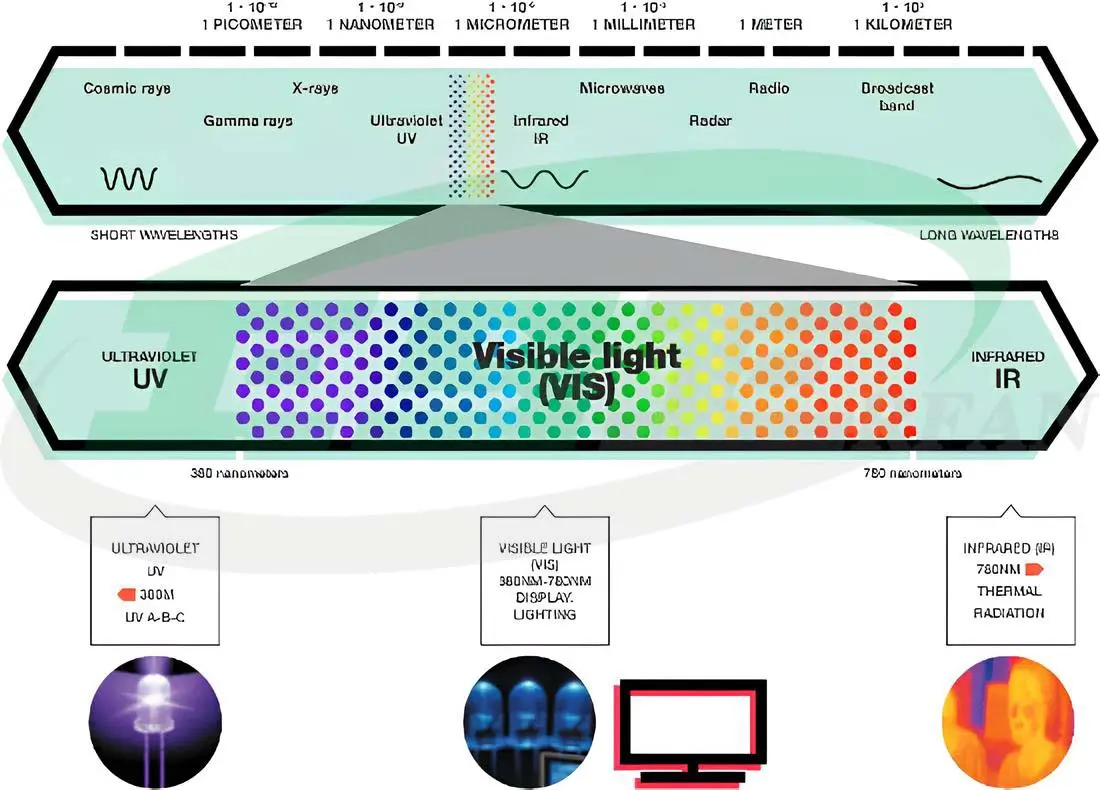
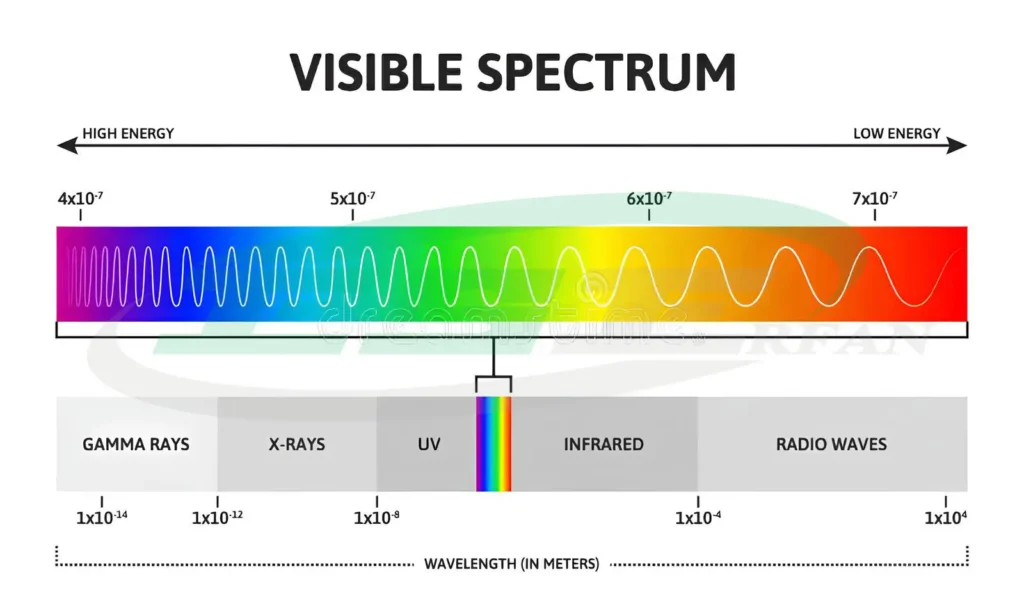
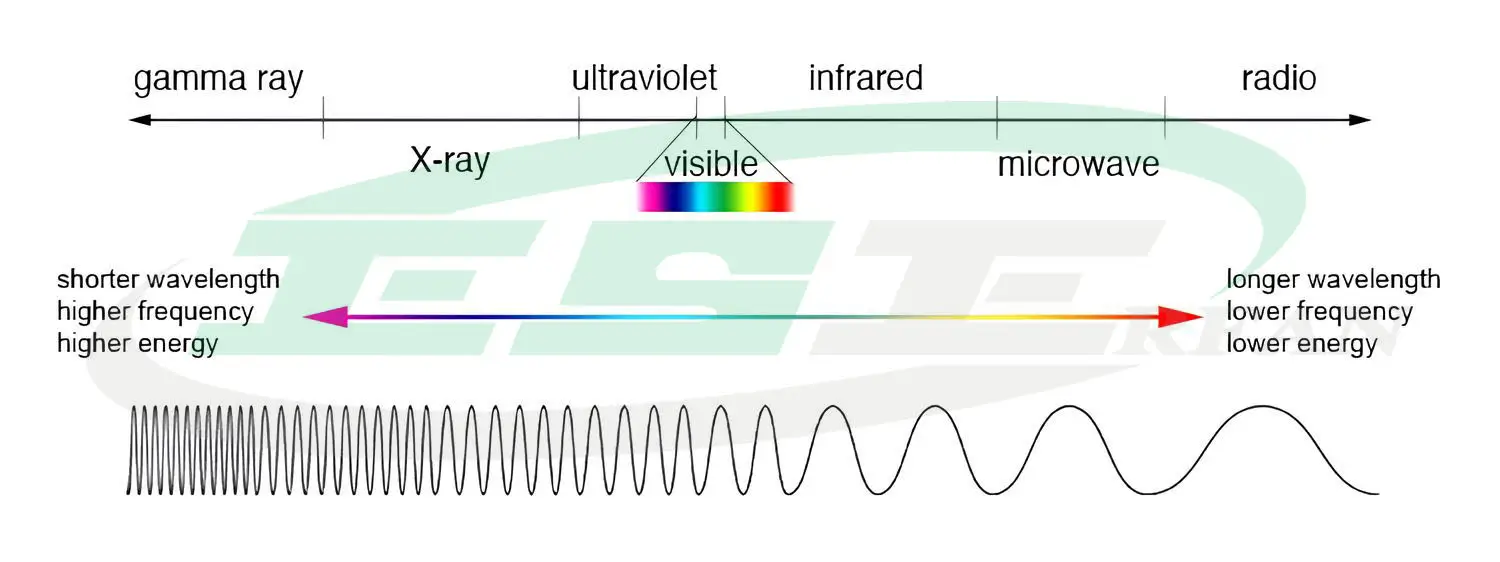
In the theory of light emission as electromagnetic waves, light is a type of electromagnetic energy. Electromagnetic waves with wavelengths of 380-780 nm that are visible to the eye are called visible light, which is a combination of different wavelengths.
The figure below shows the spectrum of electromagnetic waves and different colors:
At both ends of the visible light spectrum are infrared waves and ultraviolet radiation.
Infrared waves fall within the range of 780-1000 nm. Infrared radiation is not visible to the eye and when it hits an object, it is absorbed and converted into heat. Infrared is the main factor in the transfer of heat from the sun to the earth.
Ultraviolet radiation, abbreviated as UV, is essential for many vital activities on Earth. This radiation is emitted in the range of 100-380 nm and is divided into three groups: UV-A, UV-B, and UV-C.
The Nature of Light
UV-A spectrum causes tanning and is in the range of 315-380 nm.
UV-B spectrum causes skin redness and inflammation, sunburn, and is in the range of 280-315 nm.
UV-C spectrum is in the range of 100-280 nm and causes the destruction of cellular structures, thus it is used in purification and disinfection with radiation.
Unlike the positive effects of ultraviolet radiation (e.g., UV-B spectrum causes Vitamin D production in the body), an excessive amount of this radiation can be dangerous for the body.
The ozone layer absorbs a large amount of the sun’s ultraviolet radiation, especially the UV-C spectrum.